
With Apple and TSMC changing the game, 2016 is a turning point for the Fan-Out market. The number of enforceable patents is increasing worldwide, with several companies already standing out by virtue of their strong IP position.
Publication November 2016
| Download Flyer | Download Sample |
Report’s Key Features

- PDF > 200 slides
- Excel file (3,100+ patents)
- IP trends, including time evolutions and countries of patent filings
- Patents’ current legal status
- Ranking of main patent applicants
- IP collaboration, joint development, and licensing agreements
- Key players’ IP position, and relative strength of their patent portfolios
- Patent segmentation by technology solution (chip-first, chip-last, facedown, face-up), process steps (die placement, molding, planarization, RDL), architecture (multi-chip, PoP, SiP, face-to-face package), and technical challenge (warpage, die shift)
- Matrix showing patent applicants and their patented technologies
- Technical solutions found in patents for warpage and die-shift issues.
- FOWLP IP profiles for 18 key companies, including countries of filing, patents’ legal status, patented technologies, prior art strength index, IP blocking potential, partnerships, and IP strategy
- Excel database with all patents (3,100+) analyzed in this report, including technology segmentation
All our packaging technology patent landscapes. KnowMade performs several types of patent analysis, including patent landscapes.
Related packaging technology patent landscapes. Advance your patent strategy with our custom studies and in-depth patent landscape analysis.
Fan-out IP landscape is the most dynamic in advanced packaging
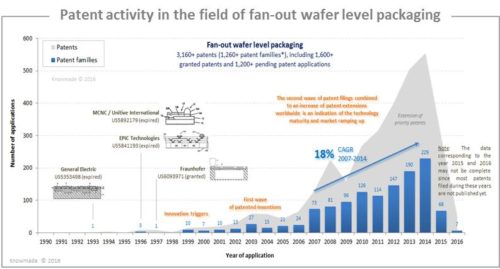
With Apple and its A10 processor employing TSMC’s InFO-PoP technology, the fan-out market has exploded. Apple’s involvement will undoubtedly generate increased interest in the fan-out platform, and market revenue is forecast to reach around US$2.5B in 2021, with 80% growth between 2015 – 2017 (See Yole Développement’s August 2016 report, Fan-out: Technology & Market Trends 2016). Moreover, following the high-volume adoption of InFO and the further development of fan-out wafer level packaging technologies, a wave of new players may enter the market. The supply chain is also expected to evolve, with a considerable amount of investment in Fan-Out packaging capabilities. In such a fast-growing Fan-Out market, it is essential to deeply understand the global patent landscape in order to anticipate changes, harvest business opportunities, mitigate risks, and make strategic decisions in order to strengthen one’s market position and maximize return on one’s IP portfolio. Knowmade has thoroughly investigated the Fan-Out packaging patent landscape (chip-first, chip-last, face-down, face-up, single-die, multi-chip module, package-on-package, system-in-package, etc.), and this report contains detailed patent analyses including countries of filing, patents’ legal status, and patented technologies, as well as patent owners, their IP position, and IP strategies. More than 3,100 patents relating to over 1,200 inventions on Fan-Out packaging have been published worldwide through September 2016, coming from 100+ patent applicants. A first wave of patent applications occurred from 1999-2006, induced by Infineon. Patent applications have increased since then, with Freescale (NXP), STATS ChipPAC (JCET), SPIL, Amkor, and TSMC entering the Fan-Out IP arena. Today the number of enforceable patents is increasing worldwide, with several companies already standing out by virtue of their strong IP position. All of major players involved has filed patents on Fan-Out packaging, except for Nanium, which does not file any patents at all but instead has adopted a different IP strategy that we discuss in this report. Another special case is the presence of patent licensing companies like Polaris Innovations (WiLAN), which in 2015 acquired key patents from Infineon/Qimonda. The visibility of such companies in the patent landscape is a tangible sign of the market explodes. In the next few years Polaris Innovations could assert its patents to make money, and in this report we present its most critical patents. We have also noted Samsung’s conspicuous IP presence in the FOWLP patent landscape, despite the company’s unclear market position. R&D labs are also present (i.e. Fraunhofer, A*STAR, CEA), but to a lesser extent. Most new entrants in the FOWLP patent landscape are Chinese players (HuaTian Technology, NCAP, SMIC), and more recently we have observed Apple’s appearance. Apple, which this year chose TSMC’s InFO-PoP technology for its A10 APE, has recently filed some patents on Fan-Out wafer level packaging (chip-last, chip-first, PoP, and SiP), reflecting a genuine interest in the FOWLP platform.
Know the key players’ IP position
This report analyzes in detail the IP status and IP strategies of key players and provides an understanding of their patented technologies. This report also provides a ranking and analysis of the top patent holders’ relative strength, derived from their portfolio size, patent citation networks, countries of patent filing, and patents’ current legal status. Furthermore, we reveal the IP strength of the key IP players involved in FOWLP technologies, and we depict their competitive IP position. JCET/STATS ChipPAC and TSMC lead the FOWLP patent landscape. From a quantitative point of view, TSMC is the most prolific patent applicant of the last few years, but according to our analyses, JCET/STATS ChipPAC has by far the strongest IP position. The company has formidable “IP blocking potential” that empowers it to deter other players to patent inventions that are similar to its own IP portfolio. TSMC is the most serious IP challenger, and it may reshape the patent landscape in the near future upon the approval of its numerous pending patent applications. Both companies feature a large enforceable patent portfolio and a long remaining lifetime of their patents.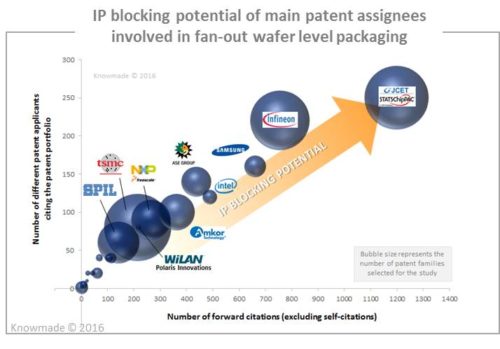
Patented technology and IP strategy
The 1,200+ inventions selected for this study are categorized by technology solution (chip-first/face-down, chip-first/face-up, chip-last), process steps (die placement, molding, planarization, RDL), architecture (multi-chip module, PoP, SiP, face-to-face package, etc.) and technical challenges (warpage, die shift). In this report we also reveal the IP strategy and technical choices of the main patent assignees. A special focus is placed on technical solutions found in patents for solving warpage and die shift issues. This report also provides an IP profile for 18 key players: Infineon, NXP/Freescale, STATS ChipPAC, TSMC, ASE, Deca Technologies, Nepes, Nanium, SPIL, Amkor, Powertech Technology, Intel, STMicroelectronics, Samsung, NCAP, WiLAN, 3D PLUS, and Apple. Each company’s IP profile includes the time evolution of their patent applications, a world map of granted patents and pending patent applications, and key features and strength of their patent portfolio.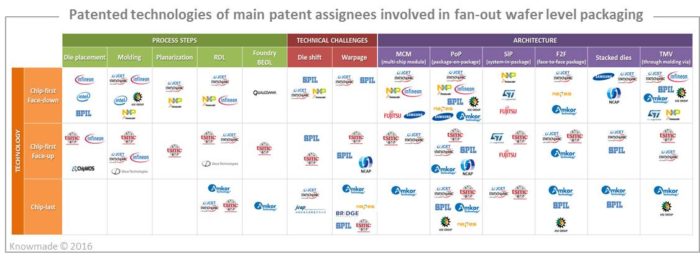
Useful patent database (3,100+ patents)
This report also includes an Excel database containing the 3,100+ patents analyzed in our study. This useful patent database allows for multi-criteria searches and includes patent publication number, hyperlinks to the original documents, priority date, title, abstract, patent assignees, technological segments, and legal status for each patent family member.
Companies mentioned in the report
3D Plus, A*STAR, ACE Technology, ADL Engineering, Altera, Amkor, Apple, ASE, Avago Technologies, Bridge Semiconductor, Bridgelux, Broadcom, Camtek, CEA, Cheng Ming, ChipMOS, Cirrus Logic, Conexant Systems, Cypress Semiconductor, Dainippon Screen Manufacturing, Deca Technologies, EPIC Technologies, EV Group, Flipchip International, Fraunhofer, Fujitsu, GE Embedded Electronics, General Electric, Gerad Technologies, GlobalFoundries, Hana Micron, Hitachi Chemical, HuaTian Technology, Infineon, Intel, ITRI (Industrial Technology Research Institute), JCAP, JCET/STATS ChipPAC, J-Devices, Jiangsu University of Science & Technology, LSI Logic, Macrotech Technology, Maxim Integrated Products, MediaTek, Medtronic, Micron Technology, Murata Electronics, NCAP, Nepes, Niko Semiconductor, Nippon Electric Glass, Nitto Denko, North Star Innovations (WiLAN), NXP/Freescale, Nytell Software, Oerlikon, PacTech Packaging Technologies, Philips, Polaris Innovations (WiLAN), Powertech Technology, Princo Middle East FZE, Qimonda, Qualcomm, Renesas Electronics, Samsung Electronics, Samsung Electro Mechanics, Semiconductor Components Industries, Seoul National University (SNU), Sharp, Shinko Electric Industries, SK Hynix, SMIC, Sony, Sound Technology, SPIL, STMicroelectronics, Technische Universitat Berlin, Tera Probe, Tessera, Texas Instruments, Toray Advanced Mat Korea, Toshiba, TSMC, Ultratech, Unimicron Technology, United Microelectronics, United Test & Assembly Center, X-Celeprint, Xenogenic Development (Intellectual Ventures), Xilinx, Xintec, Zhongxin Changdian Semiconductor.
