
The GaN power market is underway. Are you ready for the global IP chess game that will follow?
Publication September 2015
| Download Flyer | Download Sample |
Report’s Key Features

- PDF > 280 slides
- IP trends including time evolution and countries of filing
- Power GaN market data and forecasts
- Ranking of main patent applicants
- Joint developments and IP collaboration network of main patent applicants
- Key patents and granted patents near expiration
- Relative strength of main companies’ IP portfolios
- Matrix showing patent applicants and patented technologies
- Segmentation of patents:
- by technology levels, including epiwafers, devices, modules and packaging,
- by technical challenges, including current collapse, E-mode and cascode,
- and by type of substrate including SiC, silicon, sapphire and bulk GaN.
- Power GaN IP profiles of 9 major companies, with key patents, technological issues, litigation, licenses, partnerships, IP strength, IP strategy and latest market news
- Excel database with all patents analyzed in the report, including technology segmentation
KnowMade power electronics patent reports. Gain a detailed picture of your patent landscape with our IP analysis and tailored studies.
Power GaN IP dynamics heralds a future ramp-up of the market
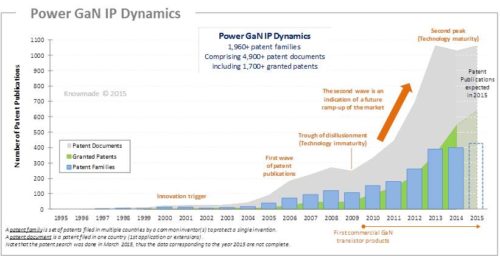
The potential energy efficiency savings from the adoption of GaN power semiconductor devices has led to significant research and development that is now beginning to be realized in commercially available devices. Today, there are only a few players selling Power GaN products (Infineon/IR, EPC, GaN Systems, Transphorm) and the market is still small, estimated at $10M in 2015 in Yole Développement’s July 2015 ‘GaN and SiC devices for power electronics applications’ report. But the ramp-up will be quite impressive, starting in 2016, at an estimated 93% CAGR through 2016-2020, with an estimated 2020 device market size of more than $300M in the baseline ‘nominal’ scenario. The GaN power industry is consolidating in preparation for this significant growth, and GaN technology is spreading across the value chain. This can been seen in recent mergers and acquisitions (Infineon/IR, Transphorm/Fujitsu’s GaN Power Conversion business), license agreements (Infineon/Panasonic, Transphorm/Furukawa) and the will of several firms to move onto the mass production stage (Transphorm/Fujitsu). As GaN power devices are now poised for rapid market adoption, a strong intellectual property (IP) position is essential for companies to grow their GaN business. In today’s Power GaN market, it is crucial to understand the global patent landscape through in-depth analyses. This enables you to anticipate changes, harvest business opportunities, mitigate risks and make strategic decisions to strengthen your market position and maximize return on your IP portfolio. More than 1,960 patented inventions related to GaN power electronics have been published worldwide up to April 2015. The first patents were published in the mid-1990s by silicon power companies (Furukawa Electric, International Rectifier, Infineon …). But the take-off of patenting activity was really observed ten years later with a first wave of patent publications over the 2005-2009 period, mainly due to American companies (International Rectifier, Power Integrations) and Japanese companies (Panasonic, Rohm, Furukawa Electric, Sumitomo Electric, Toshiba, Toyota). A second wave of patent publications started in 2010, mainly originating from Mitsubishi Electric, Fujitsu, Transphorm, Avogy and Infineon, while the first commercial products, collaborations, mergers and acquisitions emerged. Quite recently LED pure-players like Seoul Semiconductor have entered the Power GaN IP arena.
The time evolution of patent filings has reached a peak, and we expect a slowing down of new patent applications. Meanwhile, granted patents worldwide should increase after successful prosecution of the numerous pending patent applications. We believe the second peak of patent filings combined with the significant ratio of patents in force and the large number of patent applications still in the pipeline worldwide is an indication of the technology maturity heralding a future ramp-up of the GaN power market.
Identify key players and new IPchallengers
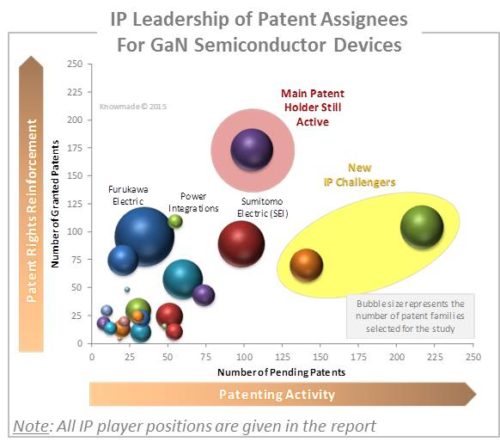
More than 200 patent applicants are involved in Power GaN IP. Most of the major silicon power players are present in the list of the top patent applicants, including International Rectifier/Infineon, Panasonic, Furukawa Electric, Sumitomo Electric, Fujitsu, Mitsubishi Electric, Toshiba, Sharp, Fuji Electric, ROHM and Power Integrations. This indicates strong interest from power players in the GaN business. So far, only IR/Infineon has commercialized GaN devices. But other traditional power players are able to disrupt and reshape the market, armed with strong IP. The report provides a ranking and analysis of the relative strength of the top patent holders derived from their portfolio size, patent citation networks, countries of patents filing and current legal status of patents. We reveal the IP strength of key Power GaN players and depict their competitive positioning. It can be safely assumed that International Rectifier (IR) has the best patent portfolio in Power GaN, and IR/Infineon combined company has the strongest IP, putting them in position to lead GaN power market growth. However, this IP leadership position could evolve in the future since newcomers like Transphorm, Fujitsu and Mitsubishi Electric are becoming major forces and may reshape the Power GaN patent landscape. Transphorm is the most important IP challenger in the Power GaN arena, ahead of other GaN start-ups like EPC and GaN Systems. Its patent portfolio and partnerships with the likes of Furukawa, Fujitsu and On Semiconductor have put it in a strong position to take a leading role in the GaN device market. Furukawa Electric has an ample IP portfolio with a significant ‘blocking potential’, but the company hasn’t been able yet to commercialize the technology on its own. By giving Transphorm exclusive licensing rights on its GaN patent portfolio, Furukawa Electric has found a strategic partner to bring its technology to market. Fujitsu and Mitsubishi Electric have demonstrated an interest in Power GaN technology since 2010 with a strong increase of their patenting activity these last 3 years, heralding substantial future IP portfolios.
Patented technology and IP strategy
The 1,960+ patented inventions selected for this study have been manually categorized by technology segment. The existing Power GaN IP covers the whole of the value chain, from epi-wafers and power semiconductor devices to discrete components, power modules, packaging, circuits and systems. The dataset of patents has been organized into various technical challenges (E-mode, cascode, E/D-mode monolithic, vertical devices, current collapse, dynamic R-on, gate charge, breakdown voltage, stray inductance, thermal issues, chip-scale package) and type of substrate for GaN epitaxy (SiC, silicon, bulk, sapphire). A special focus is provided on power semiconductor devices (transistors and diodes at the semiconductor level) and power components (discrete components, power modules and packaging). Power GaN IP is just beginning to be used as leverage by companies to negotiate licensing and supply agreements like those between Infineon and Panasonic and between Transphorm and Furukawa Electric. To this date, no litigation cases related to the Power GaN domain have been filed, but this should change as the market expands.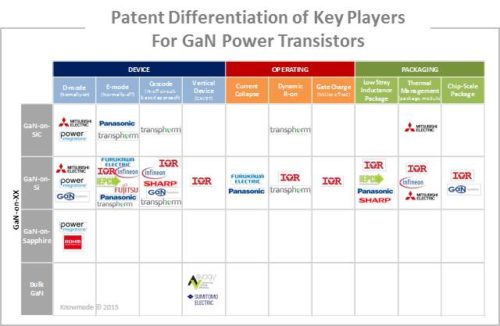
IP portfolio analysis and key patents
In our analysis, we have identified nine key players: International Rectifier (IR), Infineon, Transphorm, Fujitsu, Efficient Power Conversion (EPC), Power Integrations, GaN Systems, Panasonic and Mitsubishi Electric. For each one we provide a GaN Power IP profile including dynamics of their patent applications, key features of their patent portfolio, IP strength, collaboration network, key patents and recent patented technologies. We have identified key patents which could provide significant returns to their owners, in terms of market share, freedom of exploitation and additional revenue stream from royalties.
Useful patent database
Our report also includes an Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report with technology segmentation. This database allows for multi-criteria searches and includes patent number, legal status, priority date, title, abstract, patent assignees, technological segments, key patents and hyperlinks to the original documents.
Companies cited in the report
Alpha & Omega Semiconductor, Arkansas Power Electronics, Avogy, Cree, Daikin Industries, Delta Electronics, Dowa Electronics Materials, Efficient Power Conversion (EPC), EpiGaN, ExaGaN, Fairchild Semiconductor, Freescale, Fuji Electric, Fujitsu, Furukawa Electric, GaN Systems, General Electric, Genesic Semiconductor, Hitachi, HRL Laboratories, Infineon, International Rectifier, LG Electronics, MicroGaN, Microsemi, Mitsubishi Electric, Nissan Motor, NXP, On Semiconductor, Panasonic, Power Integrations, Renesas, Rohm, Samsung, Sanken Electric, Seoul Semiconductor, Sharp, STMicroelectronics, Sumitomo Electric, Texas Instruments, Toshiba, Toyota, Translucent, Transphorm, Triquint, TSMC, Vishay, VisIC …
