
A starting market attracting many players from various industries ; Who owns the key patents?
Publication September 2016
| Download Flyer | Download Sample |
Report’s Key Features

- PDF > 180 slides
- Excel file (3,000+ patents)
- IP trends including time evolutions and countries of patent filings
- Current legal status of patents
- Ranking of main patent applicants
- Joint developments and IP collaboration network of main patent applicants
- Key patents and granted patents near expiration
- Relative strength of maincompanies’ IP portfolios
- Matrix showing patent applicants and their patented technologies
- Segmentation of patents by:
- Technology (primary and secondarybatteries w/o lithium)
- Design (micro-batteries, solid thin film, flexible, 3D …)
- Components/materials (anode, cathode, electrolyte, barrier layer, packaging …)
- Manufacturing method (CVD, ALD, PVD, sputtering, electrodeposition, electrophoresis, sol-gel, print, spray …)
- Claimed invention (method, product, apparatus)
- Microbattery IP profiles of 10 major companies, with key patents, technological issues, partnerships, IP strength, IP strategy and latest market news
- Excel database with all patentsanalyzed in the report (3000+ patents), including technology segmentation
Discover all our patent landscapes for batteries. In-depth patent landscape and customized studies for strategic decision making.
Microbatteries IP dynamics heralds a future ramp-up of the market
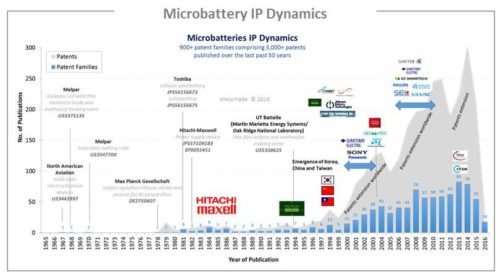
Today, micro-sized batteries are only commercialized by few companies (PowerPaper, Cymbet, Infinite Power Solutions and ST Microelectronics) while Johnson Battery Technology, Front Edge Technology and I-TEN are evaluating their micro-battery prototypes and plan to commercialize them within two years. Currently, Microbattery market is small but it should grow up within the next years, from $7m in 2015 to more than $400m in 2026 according to several published market studies. New patent applicants from various industries are looking to this starting market (STMicroelectronics, Infineon, Applied Material, Ulvac). The recent mergers and acquisitions (Apple/Infinite Power Solutions, Dyson/SAKTI3) reflect a thriving sector in transformation. Today, the number of enforceable patents has reached a critical level worldwide, several companies stand out by their strong IP position, and the first patent litigations have recently appeared. In this emerging market, a strong intellectual property (IP) position is essential for companies to grow their micro-batteries business. It is crucial to understand the global patent landscape through in depth analyses, in order to anticipate changes, harvest business opportunities, mitigate risks and make strategic decisions to strengthen one’s market position and maximize return on one’s IP portfolio. We have investigated the patent landscape of micro-batteries (micro-sized, solid thin film, flexible, 3D). More than 900 patented inventions related to micro-batteries have been published worldwide up to May 2016 by more than 300 patent applicants. The development in micro-battery field is intimately linked to batteries, microelectronics and nanomaterials fields. New battery technologies, electrodes and electrolytes materials developed for batteries in general could be adapted to micro-batteries. The first solid thin film battery was a lead battery patented in 1965 by Melpar (USA). Since 1980’s, patented microbatteries have been mainly lithium batteries. In early 1980’s, Hitachi/Hitachi-Maxell patented the first Lithium solid thin film batteries. They leaned on their knowledges and processes on batteries and thin film deposition. In 1992, Bates and his team at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) patented the sputter-based, all solid state battery utilizing the electrolyte LiPON (US 5,338,625). The patenting activity on micro-batteries really took off over the 1998- 2002 period with the creation of pure play microbattery companies (Cymbet, Polyplus Batteries, Infinite Power Solutions, Johnson Battery Technology, Front Edge Technology) and the IP involvement of Panasonic and CEA (French Research Laboratory). A second wave of patent publications started in 2007, mainly originating from semiconductor manufacturers (Semiconductor Energy Laboratory, Sumitomo) and equipment suppliers (Applied Materials, Ulvac). Currently, more than 800 patents are granted, mainly in USA and Japan, and more than 750 patent applications are pending, mainly in Europe and USA. Overall, patent filings peaked in 2013, and seem to have been slowing down since then. Meanwhile, granted patents worldwide should increase after successful processing of the numerous pending patent applications. We believe the significant ratio of patents in force and the large number of patent applications still in the pipeline worldwide is an indication of the technology maturity heralding a future ramp-up of the microbattery market.
Know the IP position of key players
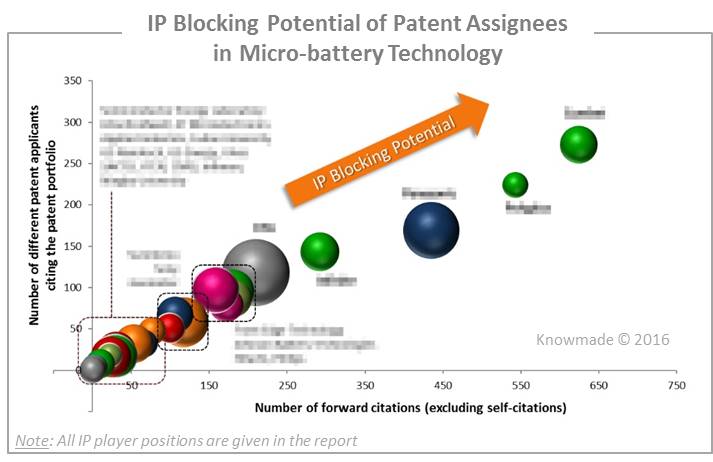
More than 300 patent applicants are involved in Microbattery IP landscape. CEA is the main patent holder around the world and is still very active in this field. But according to our analysis, Cymbet, Polyplus Battery, Infinite Power Solutions (acquired by Apple in 2013) and Panasonic have the strongest patent portfolios with a real IP blocking potential. The report provides a ranking and analysis of the relative strength of the top patent holders derived from their portfolio size, patent citation networks, countries of patent filings and current legal status of patents. We reveal the IP strength of key micro-battery players and depict their competitive positioning. In our analysis, we have identified 10 key players: Cymbet, PolyPlus Battery, Panasonic, Infinite Power Solutions, CEA, Johnson Battery Technology, Front Edge Technology, Applied Materials, I-TEN and ST Microelectronics. For each one, we provide a microbattery IP profile including dynamics and main countries of filing of their patent applications, key features of their patent portfolio, IP strength, collaboration network and key patents.
Patented technology and IP strategy
The 900+ patented inventions selected for this study have been categorized by technology segments: battery technologies (primary/secondary batteries, batteries w/o lithium…), battery designs (microbatteries, solid thin film batteries, flexible batteries, 3D batteries…), battery components (electrodes, electrolytes, packaging, barrier layers…) and used materials, and manufacturing methods/apparatus (CVD, ALD, PVD, sputtering, electrodeposition, electrophoresis, sol-gel, print, spray). A focus has been done on electrodes and electrolytes materials, manufacturing methods and 3D-batteries. For each segment, the report includes the IP dynamics of patent applications and a ranking of the main patent assignees. We describe the recent patented technologies in microbattery field, and we reveal the IP strategy and the technical choices of the main patent assignees.
Useful patent database (3,000+ patents)
Our report also includes an Excel database containing the 3,000+ patents analyzed in the study. This useful patent database allows for multi-criteria searches and includes patent publication number, hyperlinks to the original documents, priority date, title, abstract, patent assignees, technological segments and legal status for each member of the patent family.
Companies cited in the report (non-exhaustive)
A123Systems, Applied Materials, CEA, Cymbet, Fraunhofer, Front Edge Technology, Fujitsu, Geomatec, GS Energy, GS Nanotech, Hitachi-Maxell, Hongfujin precision industry, Illika Technologies, Infineon Technologies, Infinite Power Solutions, I-TEN, Johnson Battery Technology, Johnson & Johnson, KIST, MIT, NXP, Panasonic, Philips, PolyPlus Battery, PowerPaper, Robert Bosch, SAKTI3, Sony, Semiconductor Energy Laboratory, ST Microelectronics, Sumitomo, Tel Aviv University, Toshiba, Toyota, Ulvac, Varta …
