Context of healthcare technologies
Life sciences & healthcare covers a wide range of technologies, with inventions that may have various applications. Innovation can be driven either by technological advancements or societal calls for action. For example, one of the most important innovations of the past few years is the development of therapeutic mRNA technology. This major innovation was in response to the coronavirus pandemic, and today, it is being considered for many applications such as treatment for cancer, genetic diseases or infectious diseases. Its development has only just begun, and is in full expansion.
Innovation in life sciences & healthcare is supported by various players, such as fully integrated pharmaceuticals companies, universities, startups and spin-offs (from industrial or academic entities). This ecosystem of varying players, where collaborations and licenses are numerous and not often known, is complex and must be monitored and analyzed carefully. Understanding the life science & healthcare ecosystem involves answering different questions such as which new inventions to follow, newcomer identification, or the main intellectual property issues.
Life science innovation & challenges: some areas of interest for patent analysis
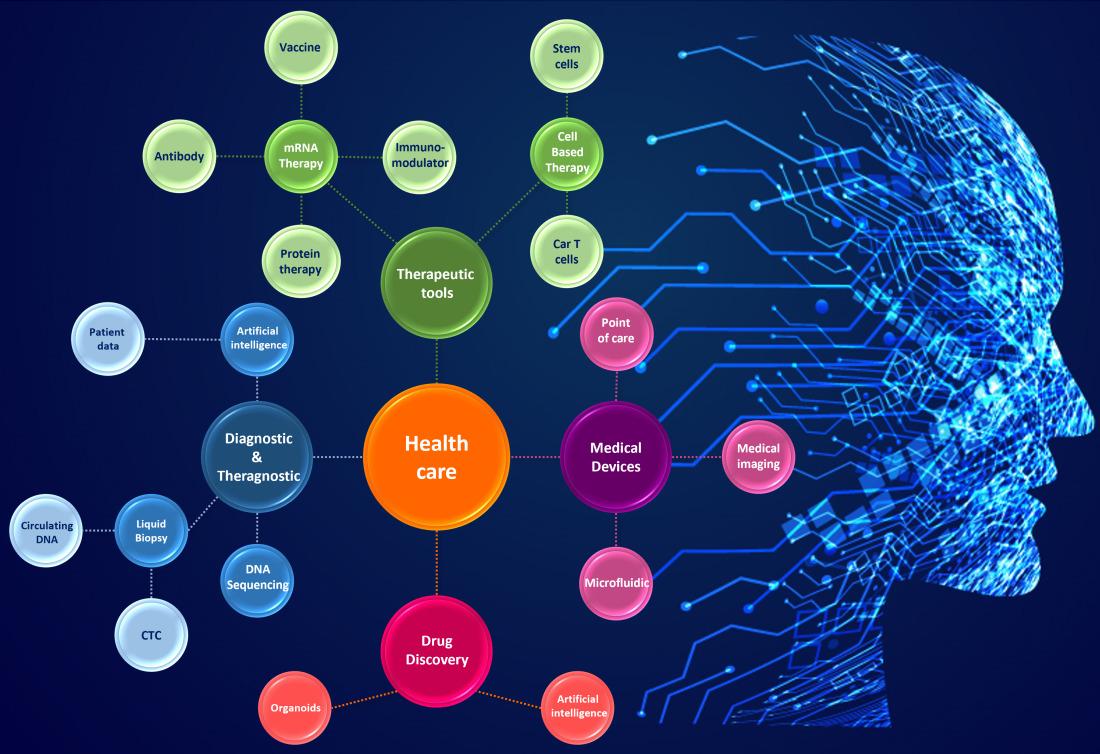
Drug discovery
From R&D to therapeutics, every step of life science innovation faces specific challenges. Innovation advances over the past two centuries have transformed drug discovery from a largely serendipitous process into the high-tech pipelines of today. Indeed, the use of a non-human model system has always represented a limitation. Innovation such as the recent development of organoids or artificial intelligence (AI) have therefore received widespread attention as having the potential to overcome this limitation. Indeed, organoids are 3D shaped structures displaying architectures and functionalities similar to in vivo organs. These organoids are developed from stem cells or organ-specific progenitors through a self-organization process; thereby, organoids are a good model for many fields of research, including drug discovery and personalized medicine. On the other hand, with the help of bioinformatics, machine learning and AI, scientists can simulate any human organ digitally. AI-driven data analytics can outline potential future avenues toward the discovery of novel mechanisms and drugs.
Medical diagnosis
An increasingly refined therapeutics approach requires the development of diagnosis & theragnosis tools. These tools have to detect a pathology, at an early stage, using a minimally invasive or non-invasive method that must be scalable. Therefore, many players are working hard on the development of liquid biopsy. This test is carried out on a blood sample and based on the detection of circulating element markers of a pathology or biological monitor (cancer, pregnancy or a transplant monitor etc.). Circulating elements can be specific cells such as circulating tumor cells (CTC) or molecules such as circulating DNA or RNA. Digital innovation also has numerous applications in diagnosis and treatment planning, with digital AI simulation of human organs like the heart, eyes, lungs or kidneys, and machine learning for imaging analysis.
New therapeutic tools
Therapeutic tools are also at the center of a flurry of innovation, recently exemplified by novel therapeutics to fight infectious diseases like the global COVID-19 pandemic, cancer, neurodegenerative or cardiovascular disease, as in personalized medicine for various conditions. Such new therapeutics tools are based on molecules like messenger RNA (mRNA), used in prophylactic or therapeutic strategies against various diseases or health conditions; chimeric antigen receptors (CAR), designed to bind to certain proteins in cancer cells; or on cell-based approaches, such as the use of stem cells in regenerative medicine, fighting cancer, correcting blood or immune disorders, etc.
Medical devices
Finally, medical devices is a dynamic field developing devices that make big improvements in how we tackle diagnosis, biological monitoring and chronic disease; how we ensure hospital safety and perform procedures. Examples of technologies of interest are high throughput DNA/RNA sequencing/synthesis (for health applications, data storage, etc.), micro-needles (painless, easiest to use and waste-free) or microfluidics (e.g., for lab-on-a chip development).
KnowMade’s purpose
Innovation in the life science & healthcare technological universe is complex, and in a state of flux as players become more dynamic. Current life sciences patent activity is a true reflection of this emulation. There are technological overlaps, and newcomers trying to make their way while large multinational players protect their freedom to operate. To decipher this landscape, and thanks to patent and technology analysis, KnowMade offers its expertise to:
- Understand and analyze trends in technological innovation
- Identify and follow new competitors and their technologies
- Identify potential risk of IP litigation
Recent reports propose studies on mRNA technology (mRNA vaccine, mRNA cancer therapies), liquid biopsies (CTC detection & isolation, circulating DNA/RNA) and medical devices (microneedles).
Latest healthcare & life sciences patent reports
Healthcare & life sciences patent monitors
Latest news on life sciences & healthcare