
The semiconductor industry has all the attributes that appeal to patent licensing companies (PLCs): Are you in their sights?
Publication February 2017
| Download Flyer | Download Sample |
Report’s Key Features

- PDF > 100 slides
- Ranking of PLCs according to their recent patent acquisitions in the semiconductor field
- Dynamics of patent acquisitions and patented technology including memory, transistor, sensor, manufacturing and packaging
- Expected expiration date of patents and remaining lifetime of PLCs’ patent portfolios
- Dynamics of US patent litigation filed by PLCs in the semiconductor market and more broadly
- Details on the latest patent litigation filed by PLC in the semiconductor field, including defendants, accused products and current status of the litigation cases
- Aggressiveness of PLCs in the semiconductor market and more broadly
- Litigation risk assessment from PLCs and potential targeted companies in the semiconductor field
- IP profiles of main PLCs
All KnowMade’s related patent reports on semiconductor technologies. Strengthen your IP strategy with our custom studies and patent landscape analysis.
PLCs will increasingly extract cash from the semiconductor industry
![]() Patent Licensing Companies (PLCs) are non-operating companies concentrated on creating the majority of their income from licensing patents to or litigating against operating companies suspected to infringe their patent rights. Other related terms include non-practicing entities (NPEs), patent holding companies (PHCs), patent monetization entities (PMEs), patent assertion entities (PAEs) and Patent Trolls. PLCs commonly acquire their patents from other companies, and then monetize them via aggressive patent litigation. Some PLCs have R&D activities in order to generate their own patents, and they monetize them by licensing. The RPX Corporation’s March 2015 report states that “NPEs cost operating companies an estimated $12.2 billion in both legal fees and other legal costs and settlement or judgment amounts in 2014”. Patent Licensing Companies operate in fields with high probability of patent infringement, mainly in USA, where litigation damages are much higher than in Europe or Asia. In a patent infringement action, the potential sales volume plays a major role for assessing the damage award. Thus, the PLCs come into action when the market has reached a critical size and target companies have made irreversible investments. Patent litigation risk tends to increase as new technologies emerge, or as existing technologies combine to create new products and services. The convergence of technologies in the semiconductor field leads to an increase in patent litigation in that sector. The semiconductor industry brings together all ingredients to appeal to PLCs. These include strong consolidation, with many mergers and acquisitions (M&A), numerous patents for sale from bankrupt companies and M&A, complex patented inventions, the colossal amount of products embedding semiconductor devices, big companies, and a lot of money. All companies designing, manufacturing or marketing semiconductor-based products are potential targets for PLCs’ next patent litigation.
Patent Licensing Companies (PLCs) are non-operating companies concentrated on creating the majority of their income from licensing patents to or litigating against operating companies suspected to infringe their patent rights. Other related terms include non-practicing entities (NPEs), patent holding companies (PHCs), patent monetization entities (PMEs), patent assertion entities (PAEs) and Patent Trolls. PLCs commonly acquire their patents from other companies, and then monetize them via aggressive patent litigation. Some PLCs have R&D activities in order to generate their own patents, and they monetize them by licensing. The RPX Corporation’s March 2015 report states that “NPEs cost operating companies an estimated $12.2 billion in both legal fees and other legal costs and settlement or judgment amounts in 2014”. Patent Licensing Companies operate in fields with high probability of patent infringement, mainly in USA, where litigation damages are much higher than in Europe or Asia. In a patent infringement action, the potential sales volume plays a major role for assessing the damage award. Thus, the PLCs come into action when the market has reached a critical size and target companies have made irreversible investments. Patent litigation risk tends to increase as new technologies emerge, or as existing technologies combine to create new products and services. The convergence of technologies in the semiconductor field leads to an increase in patent litigation in that sector. The semiconductor industry brings together all ingredients to appeal to PLCs. These include strong consolidation, with many mergers and acquisitions (M&A), numerous patents for sale from bankrupt companies and M&A, complex patented inventions, the colossal amount of products embedding semiconductor devices, big companies, and a lot of money. All companies designing, manufacturing or marketing semiconductor-based products are potential targets for PLCs’ next patent litigation.
In this report we reveal the most aggressive Patent Licensing Companies in the semiconductor field, their recent patent acquisitions, and their potential targets for future patent litigation. More than 2,880 semiconductor-related US patents have been acquired by PLCs since 2013. Now, it is a critical time to assess the patent litigation risks and know the potential targets related to these recent patent acquisitions:
Aggressiveness and litigation risks from patent licensing companies
This report provides an in-depth analysis of patent litigation filed by PLCs involved in the semiconductor field, including the dynamics of US patent litigation, defendants, accused products and the current status of the litigation cases. We have evaluated both the aggressiveness and the litigation risk from each PLC. According to our analysis, seven PLCs may be considered as major threats to practicing companies involved in the semiconductor market: WiLAN, Acacia Research, Conversant IP Management, Intellectual Ventures, Rambus, Round Rock Research and Tessera. Some of them have shown strong patent enforcement activity since 2014, and they will continue to aggressively enforce their patents against semiconductor players over the next few years.
Identify potential targeted companies
Many industrial companies at every level of the semiconductor supply chain, including integrated device manufacturers, outsourced semiconductor assembly and test companies, and equipment and material suppliers are potential targets for Patent Licensing Companies. For each PLC, we provide a detailed IP profile of their recent patent acquisitions in the semiconductor field, including:
- Which PLCs recently acquired semiconductorrelated patents?
- Which PLCs represent the biggest threat for operating companies?
- Which products and which companies have already been involved in patent litigation with PLCs in the semiconductor field?
- Which companies are potential targets for PLCs?
- How can operating companies deal with the PLC threat?
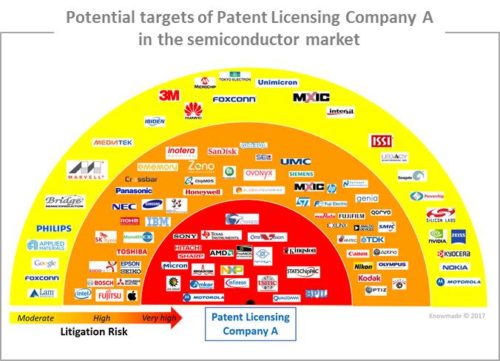
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive)
Acacia Research, Conversant IP Management, DSS Technology Management, Future Link Systems, Intellectual Ventures, Mosaid, PACT XPP Technologies, Rambus, Round Rock Research, Tessera, WiLAN, X2Y Attenuators, 3M, Advanced Micro Devices, Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Alpha & Omega Semiconductor, Altera, American PCS Communications, Amkor Technology, Analog Devices, Aplus Flash Technology, Apple, Applied Materials, Aptina Imaging, AT&T, Attopsemi Technology, AU Optronics, Avalanche Technology, Blackberry, BOE Technology, Bridge Semiconductor, Broadcom, Canon, Carl Zeiss, Chipmos Technologies, Cisco Systems, Citizen Electronics, Cordis, Cree, Crocus Technology, Crossbar, Cypress Semiconductor, Dell, Denso, Dongbu Electronics, Dongbu Hitek, Elpida Memory, Emcore, Ememory Technology, Epistar, Ericsson, Everspin, Foxconn, Fuji Electric, Fujifilm, Fujitsu, Freescale, Genia Technologies, Global OLED Technology, Globalfoundries, Google, Greatbatch, Guardian Industries, Hewlett Packard, Hitachi, Honeywell, HSIO Technologies, Huawei Technologies, Ibiden, IBM, Infineon Technologies, Innolux, Innovative Silicon ISI, Inotera Memories, Intel, Interdigital Technology, Intersil, Intuitive Surgical, Invensense, Kingston Technology, KLA Tencor, Kodak, Kyocera, Lam Research, Lattice Semiconductor, Legacy Electronics, Lexmark International, LG, Alcatel-Lucent, Macronix International, Marvell, Mediatek, Micron Technology, Microsemi, Mitsubishi Electric, Molecular Imprints, Monolithic 3D, Motorola, Murata Manufacturing, Nanometrics, Nantero, Nanya Technology, National Semiconductor, NEC, Nikon, Nokia, Nvidia, NXP, OEP Imaging, Olympus, Omnivision Technologies, Optiz, Osram, Ovonyx Memory Technology, Panasonic, Pelican Imaging, Philips, Pixart Imaging, PolyIC, Power Integrations, Powerchip Technology, Promos Technologies, Qorvo, Qualcomm, Quarkstar, Raytheon, Renesas Electronics, Ricoh, Robert Bosch, Rohm, Samsung Electronics, Sandisk, Seagate Technology, Seiko Epson, Semiconductor Energy Laboratory, Semiconductor Manufacturing International, Sharp, Siemens, Silicon Laboratories, Microchip, SK Hynix, Socionext, Sony, SPIL, STMicroelectronics, STATS ChipPAC, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSMC), Tarana Wireless, TDK, Tela Innovations, Texas Instruments, Tokyo Electron, Toshiba, Unimicron Technology, UMC, United Technologies, Universal Display, Verizon, Visera Technologies, Vishay, Xerox, Xilinx, Xintec, Zeno Semiconductor, Zink
