Are there specific memory technologies claimed in patents that are more suitable than others for artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) applications? Who are the key patent owners and the most active patent applicants in the field?
Publication January 2023
| Download Flyer | Download Sample |
Report’s Key Features
- PDF>100 slides
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report (>1,300 patent families), including patent segmentations and hyperlinks to an updated online database.
- Describing the global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.

- Identifying the main patent assignees and the IP newcomers in the different segments.
- Determining the status of their patenting activity (active / inactive) and their IP dynamics (ramping up, slowing down, steady).
- Identifying the IP collaborations (patent co-filings) and IP transfers (changes of patent ownership).
- Patents categorized into 9 segments according to technologies developed for neuromorphic computation: ReRAM, PCM, MRAM, FRAM/FeFET, Flash, DRAM, SRAM, etc.
- IP profile of 8 key IP players: patent portfolio overview (IP dynamics, segmentation, legal status, geographic coverage, etc.), IP collaborations, key patents, and recent patenting activity.
KnowMade patent landscapes on semiconductors. Enhance your competitive advantage with our patent landscape and custom studies.
Report context
In recent years, neuromorphic computing has emerged as a promising technology in the post-Moore’s law era. Neuromorphic computing systems are highly connected and parallel and consume relatively low power and processes in memory. Artificial neurons and synapses that mimic biological ones are needed to implement such a system on hardware. Both must be power-efficient, scalable, and capable of implementing relevant learning rules to facilitate large-scale neuromorphic functions. To this end, numerous efforts have been made over the last few years to create artificial neurons and synapses using emerging memories, including magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM), phase-change memory (PCM), resistive random-access memory (ReRAM or memristors), conductive bridging random-access memory (CB-RAM), ferroelectric random-access memory (FeRAM), ferroelectric field-effect transistor (FeFET), synaptic transistors, and others.
In this context, Knowmade is releasing a new report that aims to provide a comprehensive view of the patent landscape related to memory technologies for artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) applications, from materials and devices to the systems and methods that use them, categorized into memory technologies (ReRAM, PCM, MRAM, FRAM/FeFET, Flash, DRAM, SRAM, etc.).
In this report, we aim to answer the following questions:
- Is there a specific memory technology more suitable than others for artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML)?
- Who are the main patent owners and patent applicants in the field?
- What are the technical challenges targeted in patents, and what is protected (device, system, method, etc.)?
- Are there memory properties developed more specifically for intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML)?
Patent landscape analysis is a powerful tool for understanding the competitive and technological environment. It makes it possible to identify new players in emerging industries long before they enter the market while providing a better understanding of their expertise and know-how of a specific technology. Overall, patenting activity (patent filings) reflects the level of R&D investment made by a country or player in a specific technology while providing clues as to the technology readiness level reached by the main IP players. What’s more, the technology coverage and the geographical coverage of the patent portfolios are closely related to the business strategy of IP players.
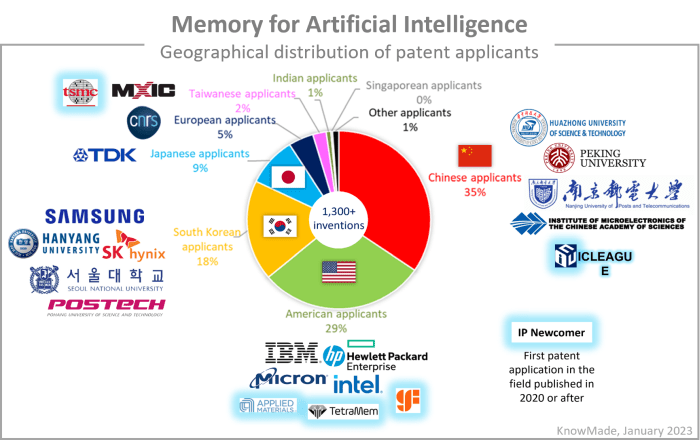
A diversified ecosystem of semiconductor companies
A mix of IC and memory players, universities, and R&D centers are competing for innovation at all stages of the R&D ladder. Industrial companies’ patenting activity took off in 2015 after R&D efforts were focused on research and fundamental physics knowledge. American and Korean industrials and Chinese and Korean universities mainly hold patents. Top patent assignees are well-established semiconductor companies, and IBM and Samsung have a leading IP position. New players such as Applied Materials, TSMC, GlobalFoundries, TetraMem, and ICLeague are entering the game, and their intellectual property (IP) may become important in the coming years.
Patent segmentation
The patents have been categorized according to the memory technologies developed for neuromorphic computation: resistance-based emerging memory technology (ReRAM, PCM, MRAM), polarization-based emerging memory technology (FRAM/FeFET), traditional memory technologies (Flash, DRAM, SRAM), other memory technologies (synaptic ionic transistor, devices based on 2D or 1D materials, hybrid materials, perovskites, nanoparticles, quantum physics, organic materials, skyrmions, etc.), and not specific (type of memory technology not specified).
All emerging memories are currently under investigation, with an upward trend for protecting FRAM in recent years. RRAM is the technology with the most inventions and the most significant number of enforceable patents worldwide.
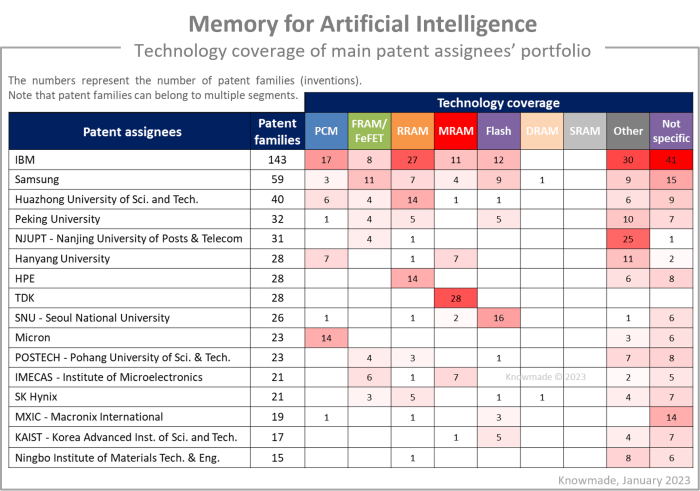
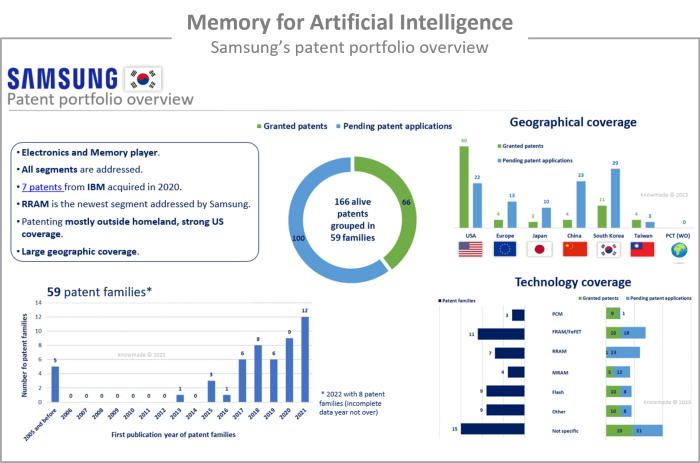
IP profiles: focus on the top IP players’ patent portfolios
The IP report includes the IP profile of eight key IP players: IBM, Samsung, Applied Materials, TDK, SK hynix, Macronix, HP, and TetraMem.
Each player’s patent portfolio related to memory technologies for AI applications is analyzed to provide an overview of its strengths, potential for reinforcement, level of IP activity, main IP collaborations, recent patenting activity, and inventions that stand out.
Useful Excel patent database
This report includes an extensive Excel database with the 1,300+ patent families (inventions) analyzed in this study. This useful patent database allows for multicriteria searches and includes patent publication numbers, hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), priority date, title, abstract, patent assignees, patent’s current legal status, and nine segments (RRAM, PCM, MRAM, FeRAM/FeFET, Flash, DRAM, SRAM, other, not specific).
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive)
Industrials: IBM, Samsung, HP, TDK, Micron, SK Hynix, Macronix, Intel, TetraMem, GlobalFoundries, Fujitsu, Thales, Panasonic, Sony, Toshiba/Kioxia, Applied Materials, Winbond Electronics, Honeywell, Monolithic 3D, Qualcomm, TSMC, Gyrfalcon, I & F, ICLeague, Merck, NTT, Olympus, Rohm, HRL Labs, Semron, Synopsys, Texas Instruments, Western Digital, Crossbar, Weeebit, Nantero, etc.
Research organizations: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Peking University, Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications (NJUPT), Hanyang University, Seoul National University (SNU), Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Institute of Microelectronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMECAS), Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering (NIMTE), Tsinghua University, CNRS – French National Research Center, Fudan University, Nanjing University, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Hebei University, Beihang University, Fuzhou University, University of Nankai (NKU), Shandong University of Science and Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Kookmin University, California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Harvard University, CEA – French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission, etc.
